


Next: Solution of the Diffusion
Up: APC591 Tutorial 5: Numerical
Previous: Introduction
The diffusion equation for a concentration 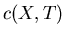 of some chemical
(given by number of particles/unit length) is
of some chemical
(given by number of particles/unit length) is
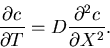 |
(1) |
Suppose that our domain is the box 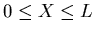 .
.
Let's define new variables 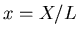 and
and 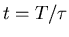 . Then,
. Then,
so equation (1) becomes
Choosing 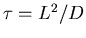 , we obtain the equation for the concentration
, we obtain the equation for the concentration 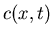
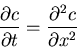 |
(2) |
on the domain 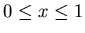 .
.
To make this equation well-posed, we need to specify the boundary conditions
at 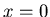 and
and 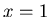 . The two main cases of interest are
. The two main cases of interest are
- Constant concentration boundary conditions:
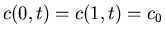 . Such
boundary conditions might be due to the contact of the edges of our domain
with an ``infinite'' reservoir with essentially constant concentration
. Such
boundary conditions might be due to the contact of the edges of our domain
with an ``infinite'' reservoir with essentially constant concentration 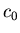 .
.
- No-flux boundary conditions:
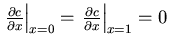 . Such boundary
conditions correspond to having no flux out of the domain.
. Such boundary
conditions correspond to having no flux out of the domain.



Next: Solution of the Diffusion
Up: APC591 Tutorial 5: Numerical
Previous: Introduction
Jeffrey M. Moehlis
2001-10-24
![]() of some chemical
(given by number of particles/unit length) is
of some chemical
(given by number of particles/unit length) is
![]() and
and ![]() . Then,
. Then,
![]() and
and ![]() . The two main cases of interest are
. The two main cases of interest are